Simple Tips About Can DC Convert To AC

The Curious Case of DC Turning into AC
1. Unveiling the Transformation
Alright, let's tackle a question that pops up more often than you'd think: Can Direct Current (DC) actually transform into Alternating Current (AC)? The short answer? Absolutely! But like most things in the world of electricity, there's a bit more to the story than just a simple "yes." Think of it like this: DC is like a calm, steady stream, while AC is like ocean waves — constantly changing direction.
The reason this question even arises is because, at their core, DC and AC are fundamentally different. DC, as the name implies, flows in one direction only. Batteries are a prime example; they consistently pump out electricity in a single, predictable path. AC, on the other hand, oscillates, switching direction many times a second. This is what powers your home, with the current flipping back and forth dozens of times every blink of an eye.
So how do we bridge the gap between these two electrical personalities? Enter the inverter. This clever little device is the unsung hero that takes DC power, like what you get from solar panels or a battery, and converts it into AC power that can run your appliances or even be fed back into the power grid. Inverters come in various shapes and sizes, from the small ones that power your laptop to the massive ones used in solar farms.
The magic happens inside the inverter thanks to some clever electronic circuitry, primarily using transistors and other components. These components rapidly switch the DC current on and off, creating a stepped waveform that approximates AC. This stepped waveform is then often smoothed out using capacitors and inductors to produce a cleaner, more sinusoidal AC output. Think of it like taking a bumpy road and paving it over to make it smooth — the destination is the same, but the journey is much more pleasant.
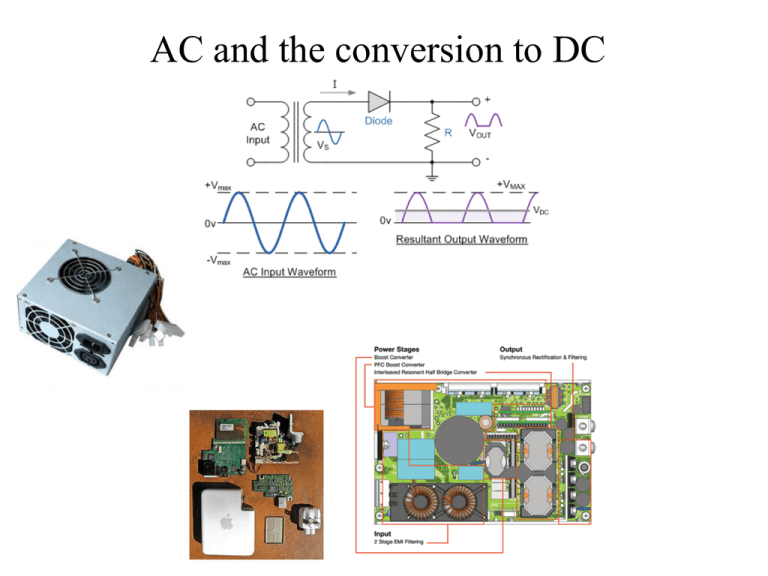
AC DC Conversion
Inverters
2. How Inverters Work
Now, let's delve a bit deeper into how these inverters actually pull off this amazing feat. Imagine you have a bucket of water (DC power) and you need to make it flow back and forth (AC power). An inverter, in essence, acts like a series of strategically placed valves that open and close in rapid succession. These valves control the flow of DC electricity, directing it first in one direction and then in the other, creating the alternating current.
The core components of an inverter are switches, usually transistors, which are controlled by a circuit that precisely times their opening and closing. By carefully coordinating these switches, the inverter can create a square wave, which is a crude approximation of AC. However, most inverters then employ filters and other circuits to smooth out this square wave into a smoother sine wave, which is more efficient and compatible with most electrical devices.
There are different types of inverters, each with its own pros and cons. For example, a modified sine wave inverter produces a waveform that is closer to a sine wave than a square wave, but still not perfect. These are typically less expensive but may not work well with all appliances. A pure sine wave inverter, on the other hand, produces a waveform that is virtually identical to the AC power you get from the grid. These are more expensive but provide the best performance and compatibility.
The efficiency of an inverter is also a crucial factor to consider. An efficient inverter will convert more of the DC power into AC power, wasting less energy in the process. This is particularly important for applications like solar power, where every watt counts. Look for inverters with high efficiency ratings to maximize your energy savings.

Why Bother Converting DC to AC Anyway?
3. The Advantages of AC Power
So, if DC is so simple and straightforward, why do we even bother converting it to AC in the first place? The answer lies in the way AC power can be transmitted over long distances. AC voltage can be easily stepped up or down using transformers. This allows electricity to be transmitted at high voltages, which reduces current and minimizes energy losses due to resistance in the wires. Think of it like shipping water in a small pipe versus a huge pipe — the bigger pipe (higher voltage, lower current) gets the water there with less loss.
When electricity is transmitted over long distances at high voltage, it can then be stepped down to lower voltages for use in homes and businesses. This is why you see transformers on power poles — they are reducing the high-voltage AC power from the transmission lines to the lower voltage AC power that is used in your house.
Another advantage of AC power is that it is easier to generate. Most large-scale power plants, whether they use coal, nuclear power, or hydropower, generate AC electricity. This is because the generators used in these plants are designed to produce AC power directly.
While DC power has its place in batteries, electronics, and some specialized applications, AC power remains the dominant form of electricity for most of the world. Its ability to be efficiently transmitted and easily transformed makes it the ideal choice for large-scale power distribution.

Real-World Examples of DC to AC Conversion
4. Inverters in Action
Alright, let's bring this down to earth with some real-world examples. Think about solar panels. They generate DC electricity when sunlight hits them. But your house runs on AC. So, what's the bridge? You guessed it: an inverter! The inverter takes the DC electricity from the solar panels and transforms it into AC electricity that can power your lights, appliances, and even feed back into the grid, allowing you to sell excess power back to the utility company.
Another common example is uninterruptible power supplies (UPS). These devices are designed to provide backup power in the event of a power outage. They typically use batteries to store DC electricity, and an inverter to convert it to AC electricity to keep your computers and other critical equipment running during a blackout.
Even your car uses a DC to AC inverter! Many modern vehicles have inverters that allow you to plug in AC devices, such as laptops or phone chargers. These inverters take the DC electricity from the car's battery and convert it to AC electricity that can power your devices on the go.
These examples highlight the versatility of DC to AC conversion. Inverters are essential components in a wide range of applications, from renewable energy systems to backup power supplies to mobile electronics. They allow us to harness the benefits of both DC and AC power, making our lives more convenient and efficient.
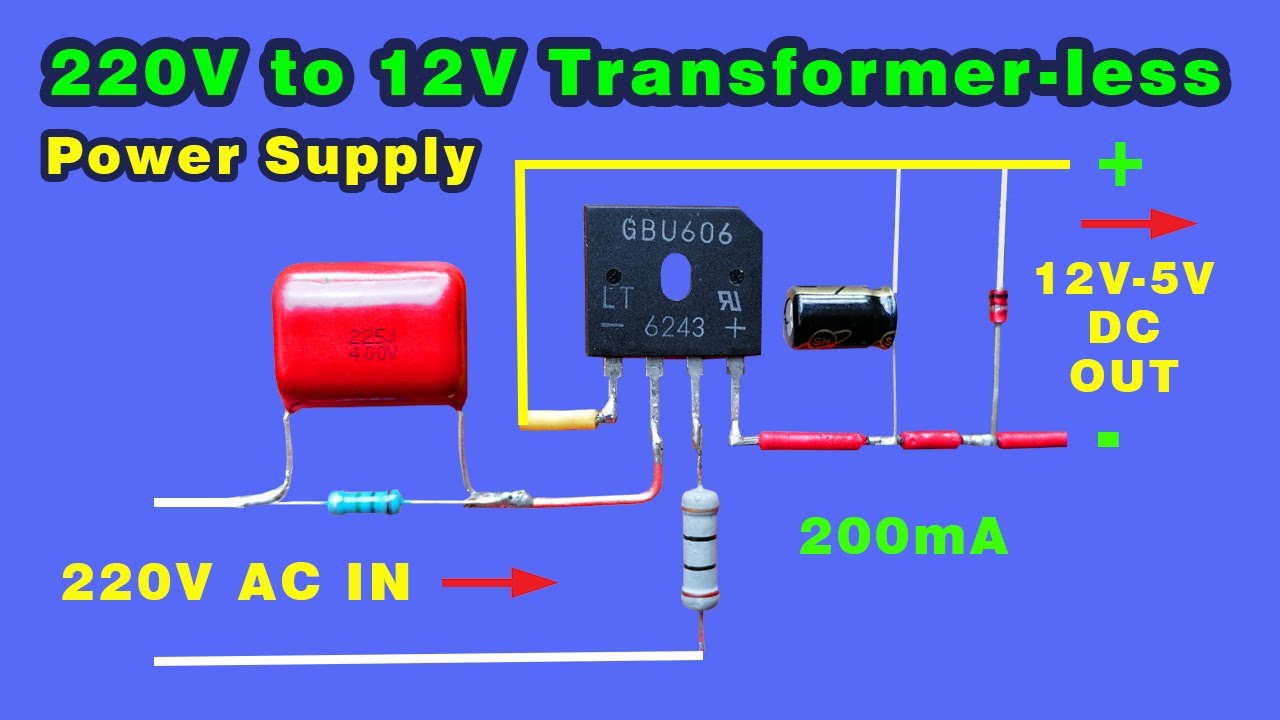
How To Convert AC DC Without Transformer, 220v 12v Dc Converter
The Future of DC to AC Conversion
5. Innovations and Improvements
The world of DC to AC conversion isn't standing still. Researchers and engineers are constantly working on improving inverter technology, making them more efficient, smaller, and more reliable. One area of focus is on improving the switching speed and efficiency of the transistors used in inverters. Faster switching speeds allow for the creation of cleaner, more sinusoidal AC waveforms, while higher efficiency reduces energy losses.
Another area of innovation is in the development of new inverter topologies. These are different circuit designs that can offer improved performance or reduced cost. For example, some new inverter designs use silicon carbide (SiC) or gallium nitride (GaN) transistors, which offer higher switching speeds and lower losses than traditional silicon transistors.
The increasing adoption of renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, is also driving innovation in inverter technology. Grid-tied inverters, which connect renewable energy systems to the power grid, are becoming increasingly sophisticated, with features such as advanced grid support and reactive power control.
As battery technology continues to improve, the demand for DC to AC inverters will likely increase as well. Battery-powered devices, such as electric vehicles and energy storage systems, require inverters to convert the DC power from the batteries to AC power for use in homes and businesses. The future of DC to AC conversion is bright, with ongoing innovations promising to make inverters even more efficient, reliable, and versatile.
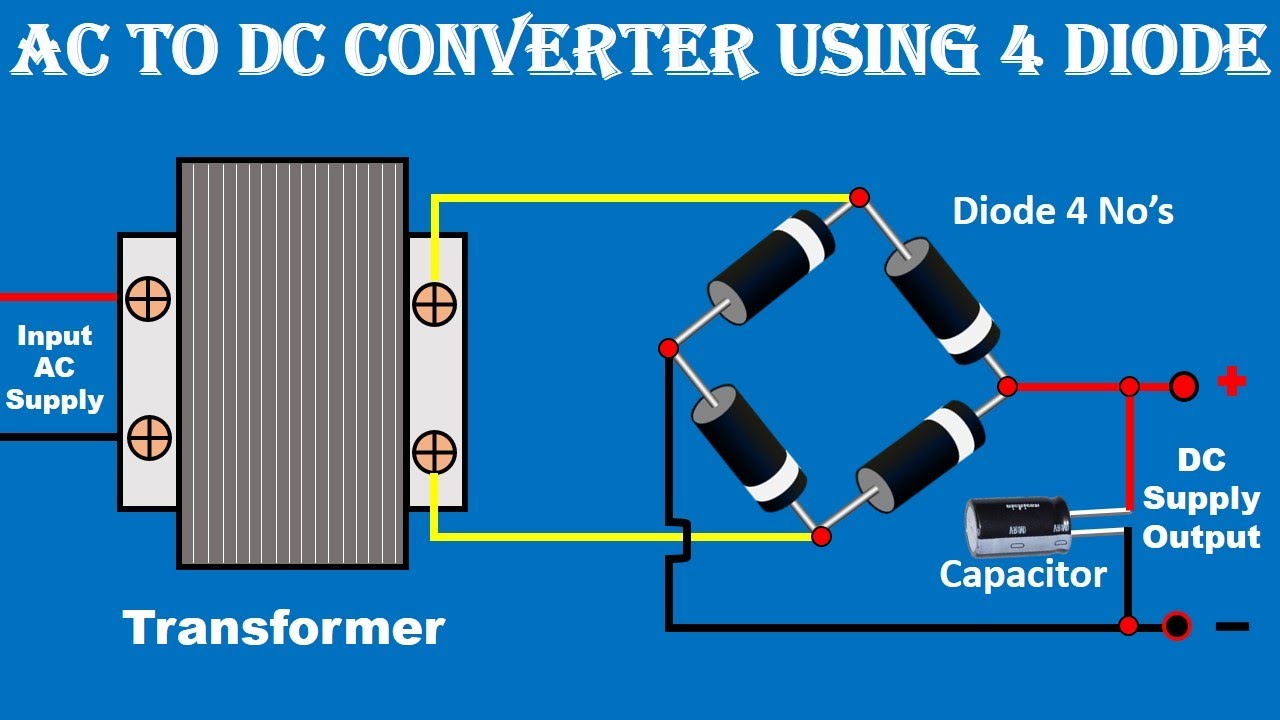
Simple Ac To Dc Converter
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
6. Your Burning Questions Answered
Alright, let's tackle some of those questions that are likely buzzing around in your head. After all, even electricity can be confusing sometimes!
Q: Can I use any inverter with any appliance?
A: Not necessarily. It's important to match the inverter's power rating to the appliance's power consumption. Also, some appliances are more sensitive to the type of AC waveform produced by the inverter. Pure sine wave inverters are generally compatible with all appliances, while modified sine wave inverters may not work well with some devices.Q: How long will an inverter last?
A: The lifespan of an inverter depends on several factors, including the quality of the components, the operating conditions, and the amount of use. A well-made inverter that is properly maintained can last for many years. Regularly check the inverter for signs of wear and tear, and follow the manufacturer's instructions for maintenance.Q: Is it dangerous to convert DC to AC?
A: Converting DC to AC involves working with electricity, which can be dangerous if not handled properly. It's important to follow all safety precautions and to consult with a qualified electrician if you are unsure about anything. Always disconnect the power source before working on an inverter, and never tamper with the internal components of an inverter unless you are a trained professional.Q: What's the difference between a DC to AC inverter and an AC to DC converter (like a phone charger)?
A: Good question! They do the opposite thing. A DC to AC inverter takes DC power (from a battery, for example) and changes it into AC power (like what comes out of a wall socket). An AC to DC converter, on the other hand, takes AC power and changes it into DC power. Your phone charger takes the AC from the wall and converts it to the DC your phone battery needs.